
Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) are regulations that establish the minimum level of energy efficiency that a product must meet in order to be sold in a particular market. These standards are typically set by government agencies or regulatory bodies and are aimed at reducing energy consumption and promoting the use of more energy-efficient technologies.
Minimum energy performance standards (MEPS) can apply to a wide range of products, including appliances, lighting, heating and cooling systems, and vehicles.
The specific requirements for each product category may vary depending on factors such as the type of product, its intended use, and regional energy efficiency goals.
The primary objective of Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) is to encourage manufacturers to develop and produce products that consume less energy while still meeting the performance needs of consumers.
By setting minimum efficiency levels, Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) help to drive innovation in the industry and promote the adoption of more sustainable practices.
In addition to reducing energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions, Minimum Energy Performance Standards can also lead to cost savings for consumers over time.
Energy-efficient products generally consume less electricity or fuel, resulting in lower utility bills. Furthermore, these standards can contribute to national energy security by reducing dependence on imported fossil fuels.
Compliance with Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) is typically enforced through testing and certification processes carried out by authorized bodies or agencies.
Manufacturers are required to label their products with information about their energy performance ratings so that consumers can make informed choices when purchasing appliances or equipment.
In this blog, we shall understand what is Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) and how they play a crucial role in driving energy efficiency improvements across various sectors.
Also how promoting the use of more efficient technologies, these standards contribute to environmental sustainability while also benefiting consumers through reduced operating costs.
How Minimum Energy Performance Standards Are Set and Implemented?
The process of setting Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) involves various regulatory bodies, stakeholders, and compliance and enforcement mechanisms.
The process of setting and implementing Minimum Energy Performance Standards typically involves the following steps:
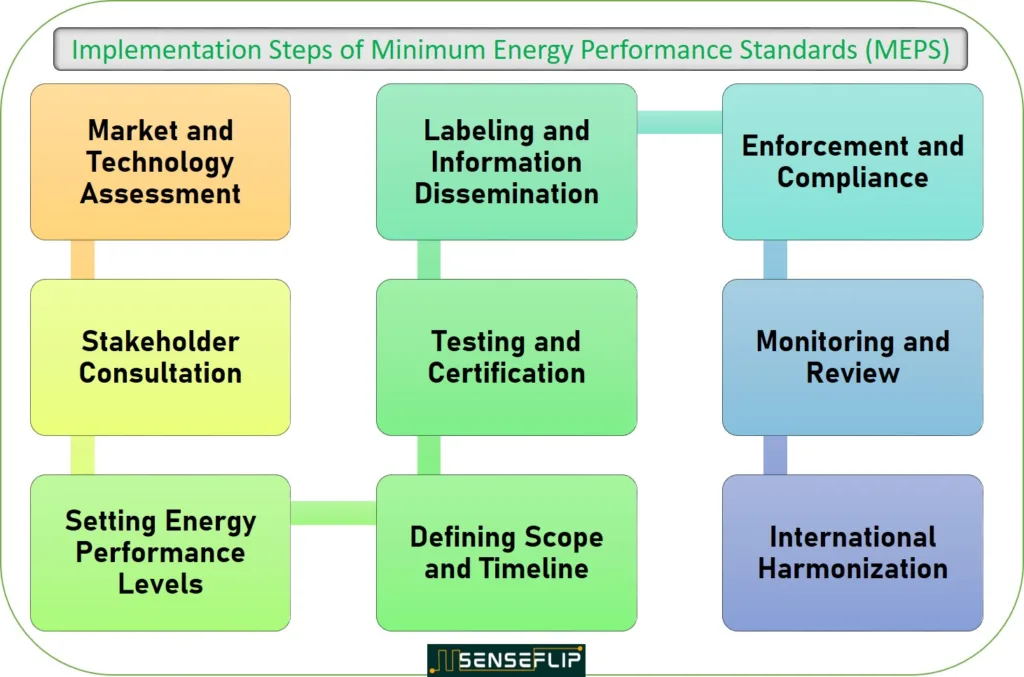
1- Market and Technology Assessment:
Governments and regulatory bodies begin by assessing the market and available technologies for the specific products or equipment they intend to regulate.
This involves studying the existing products, understanding their energy consumption levels, and identifying the most efficient technologies available.
2- Stakeholder Consultation:
Governments engage with relevant stakeholders, including manufacturers, industry associations, consumer groups, environmental organizations, and other experts, to gather insights, feedback, and concerns about the proposed Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS).
This ensures that all perspectives are considered in the development of the standards.
3- Setting Energy Performance Levels:
Based on the market and technology assessment and stakeholder input, governments set the minimum energy performance levels that products and equipment must meet to comply with the Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS).
These levels are typically expressed as energy efficiency ratings or metrics, such as energy consumption per unit of output or energy efficiency ratios.
4- Defining Scope and Timeline:
Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) typically apply to specific product categories or equipment types. The regulations define the scope of products covered by the standards and set timelines for manufacturers to meet the new requirements.
Sometimes, Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) is implemented in stages, gradually raising the efficiency levels over time.
5- Testing and Certification:
To ensure compliance with Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS), manufacturers are required to test their products and equipment in accredited laboratories.
They must provide energy efficiency data and performance ratings for their products, which are then independently verified and certified by the relevant authorities.
6- Labeling and Information Dissemination:
Many Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) programs also include labeling requirements, where products meeting the standards are labeled with energy efficiency information, helping consumers make informed choices.
This labeling often includes energy efficiency ratings, estimated annual energy consumption, and other relevant information.
7- Enforcement and Compliance:
Governments enforce Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) through various mechanisms, including market surveillance, random inspections, and penalties for non-compliant products.
Penalties may include fines, product recalls, or restrictions on non-compliant products’ sale and distribution.
8- Monitoring and Review:
Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) are periodically reviewed and updated to align with technological advancements and changes in the market.
Regular monitoring and evaluation help ensure that the standards remain effective and continue to drive energy efficiency improvements.
9- International Harmonization:
In some cases, countries may harmonize their Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) with international standards to facilitate trade and promote global energy efficiency efforts.
Overall, setting Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) involves a collaborative effort between regulatory bodies, stakeholders from various sectors, compliance mechanisms to verify adherence to standards, and enforcement measures to maintain their effectiveness.
This comprehensive approach helps promote energy efficiency while protecting consumer interests and reducing environmental impact. Non-compliant products may face penalties such as fines or even removal from the market.
The Impact of Minimum Energy Performance Standards On Different Products and Industries
Here are some examples of how Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) impact different products and industries, supported by factual data:
Appliances and Electronics
Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) have a significant impact on household appliances and electronics, such as refrigerators, washing machines, air conditioners, and televisions.
The implementation of Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) results in more energy-efficient products being available in the market, leading to reduced energy consumption and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
According to a report by the International Energy Agency (IEA) in 2019, the introduction and enforcement of Minimum Energy Performance Standards for appliances and electronics worldwide saved approximately 3,800 terawatt-hours (TWh) of electricity in 2018. This is equivalent to the annual electricity consumption of the entire European Union.
Lighting
Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) have also played a crucial role in improving the efficiency of lighting products.
The transition from traditional incandescent bulbs to compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs) and light-emitting diodes (LEDs) has been accelerated by Minimum Energy Performance Standards MEPS.
These more energy-efficient lighting options not only save energy but also have a longer lifespan, reducing waste and promoting sustainability.
A study published in the journal “Energy Policy” in 2017 analyzed the global impact of MEPS on lighting.
The researchers estimated that Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) had led to energy savings of about 2,500 TWh per year by 2010. This represents nearly 9% of global electricity consumption and is equivalent to the annual electricity consumption of India and Germany combined.
Automotive Industry
Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) are also relevant to the automotive industry, particularly for electric vehicles (EVs). These standards may mandate minimum energy efficiency levels for battery systems, electric motors, and overall vehicle performance.
By setting Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) for EVs, governments encourage automakers to improve the efficiency of their vehicles and promote the adoption of cleaner transportation options.
A report by the International Council on Clean Transportation (ICCT) in 2019 analyzed the impact of vehicle efficiency standards worldwide. It found that vehicle efficiency standards in the United States, Europe, China, and other regions had led to a reduction of approximately 230 million tons of CO2 emissions in 2018, with the potential to save 270 million tons by 2030.
Industrial Equipment
Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) also influence industrial equipment, such as motors, pumps, and compressors.
By setting minimum energy performance levels for these devices, industries are encouraged to invest in more energy-efficient equipment, leading to reduced energy consumption and operational costs.
According to a study published in the journal “Energy Efficiency” in 2016, the implementation of Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) for electric motors and motor-driven systems in the European Union resulted in electricity savings of about 259 TWh per year by 2020. This corresponds to a reduction of around 110 million tons of CO2 emissions.
The Evolution of Minimum Energy Performance Standards: Trends and Future Outlook
The evolution of Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) has been a progressive journey driven by the growing recognition of the importance of energy efficiency, environmental sustainability, and consumer cost savings.
Here are some trends and the future outlook for Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS).
Increasing Coverage and Scope
Over the years, Minimum Energy Performance Standards have expanded their coverage to encompass a broader range of products and industries.
Initially, Minimum Energy Performance Standards primarily targeted appliances like refrigerators and air conditioners. However, they now apply to a wide array of products, including lighting, motors, industrial equipment, computers, and vehicles.
The future is likely to witness further expansion, with Minimum Energy Performance Standards being extended to newer and more energy-intensive disruptive technologies, such as data centers and emerging technologies in the Internet of Things (IoT) space.
Stringency and Technology Advancements
As technology progresses, the energy efficiency potential of products also increases. To keep up with these advancements, Minimum Energy Performance Standards are becoming more stringent over time.
Governments and regulatory bodies continuously review and update the standards to set higher efficiency targets. This trend is expected to continue as manufacturers innovate and develop new, energy-efficient technologies.
Global Harmonization
The proliferation of Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) has led to variations in standards across different regions and countries.
In recent years, there has been a growing effort towards harmonization and alignment of Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) internationally.
International organizations like the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) work to establish global standards, enabling easier trade and consistent energy-saving efforts worldwide.
Market Transformation
Minimum Energy Performance Standards play a pivotal role in transforming markets by pushing manufacturers to produce more energy-efficient products.
As efficiency standards become stricter, older, less efficient products are phased out, and consumers adopt newer, more efficient alternatives. This leads to a market shift towards energy-efficient products, fostering a virtuous cycle of innovation and sustainability.
Integration with Labeling and Incentive Programs
Many countries complement Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) with energy efficiency labeling programs, like ENERGY STAR in the United States or the EU Energy Label in Europe.
These labels provide consumers with easy-to-understand information about product efficiency and help influence purchasing decisions. Governments also often incentivize the adoption of energy-efficient products through tax rebates or other financial incentives.
Focus on Climate and Environmental Goals
As the urgency to combat climate change and reduce greenhouse gas emissions intensifies, Minimum Energy Performance Standards are gaining even more significance.
Governments worldwide are aligning their Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) with climate goals, such as those outlined in the Paris Agreement.
Future Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) are likely to be designed with a more explicit focus on environmental impact, driving manufacturers to prioritize low-carbon technologies.
Embracing Digitalization
The advent of digitalization and the Internet of Things (IoT) present new opportunities to enhance energy efficiency. Future Minimum Energy Performance Standards may incorporate requirements for smart technologies, enabling better energy management, real-time monitoring, and demand response capabilities.
Challenges in Enforcement and Compliance
One of the significant challenges for the future of Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) is ensuring effective enforcement and compliance.
Governments and regulatory bodies must invest in monitoring mechanisms and collaboration with industry stakeholders to verify that products entering the market meet the required energy efficiency standards.
Achieving Compliance with Minimum Energy Performance Standards: Tips for Manufacturers and Consumers
As the world becomes more conscious of the environmental impact of energy consumption, meeting energy efficiency requirements has become a key consideration for manufacturers and importers.
By adhering to energy efficiency requirements, businesses can not only reduce their carbon footprint but also save on energy costs in the long run.
For manufacturers and importers, selecting energy-efficient products is crucial. These products are designed to consume less energy while maintaining optimal performance.
By incorporating such products into their operations, businesses can not only meet regulatory standards but also improve their overall sustainability efforts.
To assist consumers in making informed choices, labeling schemes have been introduced to identify compliant products. These labels provide valuable information regarding a product’s energy efficiency rating and its compliance with specific standards or regulations.
Consumers can easily identify and compare the energy efficiency of different products before making a purchase decision.
By choosing energy-efficient products as consumers, individuals can play an active role in reducing their own carbon footprint.
In conclusion, meeting energy efficiency requirements as a manufacturer or importer is essential for both environmental sustainability and cost savings.
Similarly, as consumers, selecting energy-efficient products contributes to personal savings and reduced ecological impact.
The availability of labeling schemes further aids in identifying compliant products that align with these objectives.
Conclusion: Harnessing The Power of Minimum Energy Performance Standards For A Sustainable Future
In conclusion, harnessing the power of Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) is crucial for achieving a sustainable future. These standards play a vital role in promoting energy efficiency and reducing the environmental impact of various products and appliances.
To fully harness the benefits of Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS), it is essential for policymakers to prioritize their implementation and enforcement. This includes regular monitoring and updating of standards based on technological advancements and market trends.
by embracing Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS), we can pave the way toward a sustainable future characterized by reduced energy consumption, lower carbon emissions, and a healthier environment for generations to come.

oNAYJjAJQKVSvDbS
pHPnUEYnPuLlXkxDDCD